- Home
- News
- Press release
- Product news
- Cooled range of sCMOS cameras including Backside illuminated models
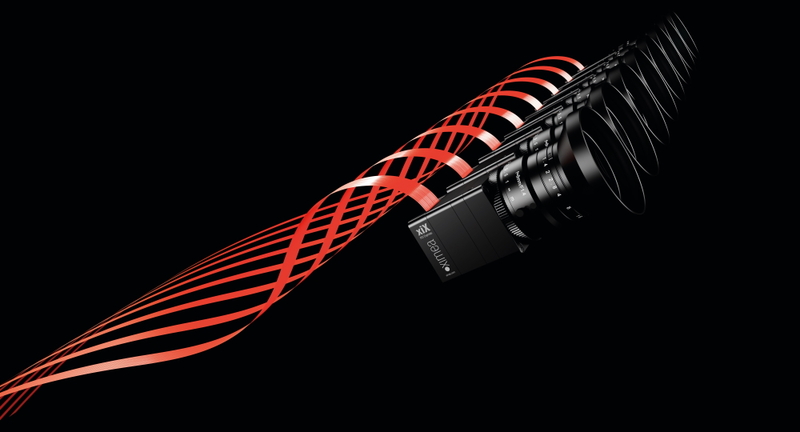
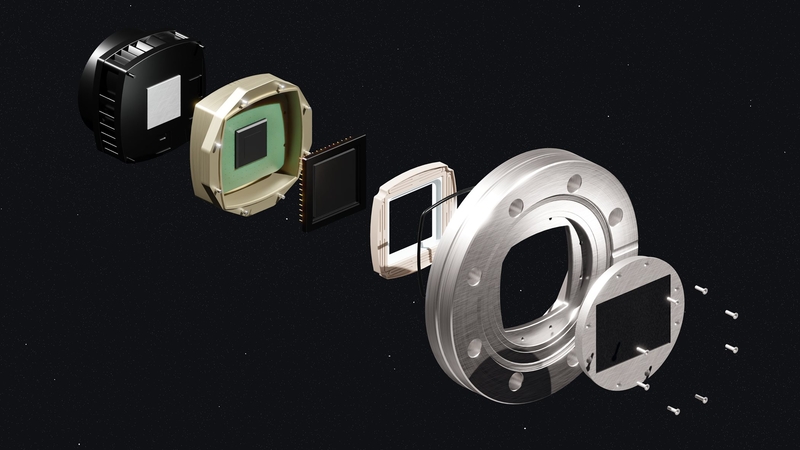
Muenster, Germany, August 08th, 2018 – Increased challenges in Scientific field and industrial applications require further enhancement in camera quality and XIMEA is preparing a combination of models based on the newest Scientific CMOS (sCMOS) sensors divided into versions with Thermoelectric Peltier cooling or PCI Express interface which delivers their full speed potential.
The whole range of cameras is equipped with sCMOS sensors handpicked from the extraordinary line introduced by Gpixel inc., concentrating on excellent low noise values, high Dynamic range and including Backside illuminated models with unbelievable Quantum efficiency numbers. To utilize these exceptional parameters the use of both Rolling and Global shutter option is available.
The Rolling shutter mode offers lowest achievable noise and highest sensitivity which results from the symbiosis of USB3 and TE cooling arranged through Peltier. The sensor models that are best for such combination are GSENSE2020BSI and GSENSE400BSIwith the Dark noise down to almost 1e- and Quantum efficiency up to 95%.
The Global shutter capture presents a compromise of the sensor sensitivity values, but really shines at frame rates which are provided with the help of PCIe interface. This is particularly useful in case of high resolution and large format sensors streaming 2x 12bit ADC. Sensors suitable for such bandwidth boost are for example GSENSE5130 and GSENSE6060BSI.
With a plethora of options like these, it is important to understand the exact requirements of the specific application. If high speed is relevant or long exposure times are critical.
Currently the cameras are in the preliminary stage and have “technical samples” status of availability.
That means, they have feature limitations and are not available from stock yet with longer lead times.
Applications examples include:
| FRET | FRAP | FISH |
| Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer | Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching | Fluorescence in situ hybridization |
| FCS | TIRF | BEC | CARS |
| Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy | Total internal reflection fluorescence | Bose-Einstein condensates | Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering |
| PALM | STORM | SPIM |
| Photoactivated localization microscopy | Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy | Single Plane Illumination Microscopy |
| NDT | OCT | NEO |
| Nondestructive testing | Optical coherence tomography | Near Earth Object detection |
Inspired? What’s Next?
Related articles



Latest articles